Bussiness
Ocean technology hub AltaSea blooms on San Pedro waterfront
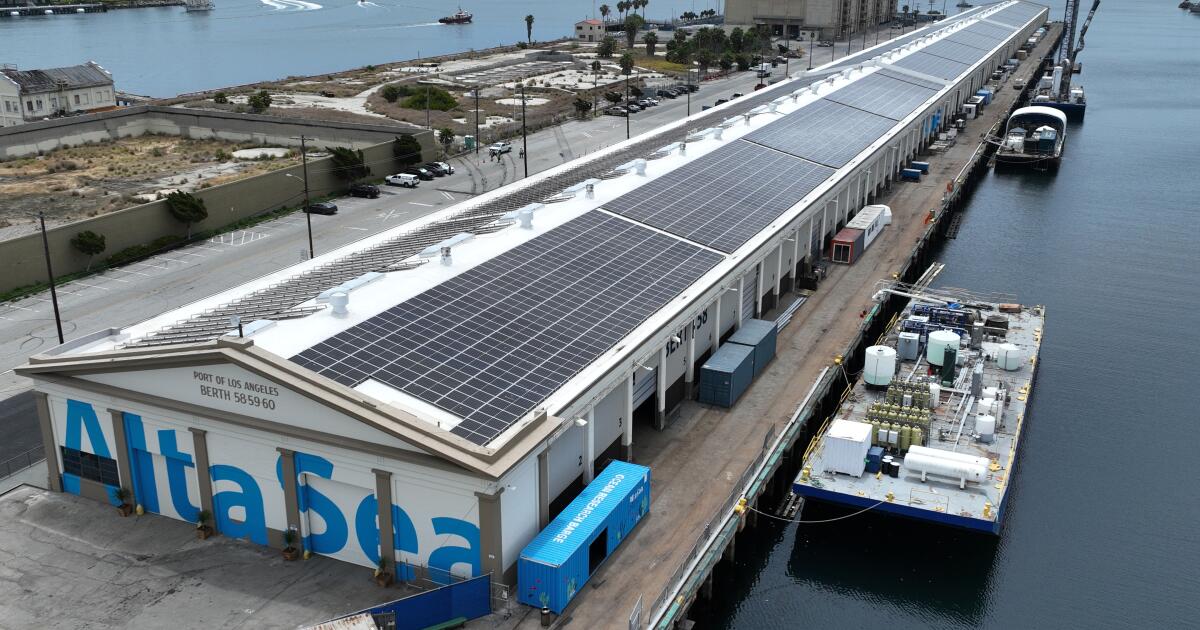

A moon shot to make Southern California an international leader in the “blue economy” is taking shape in San Pedro as a $30-million renovation of three historic waterfront warehouses nears completion.
AltaSea at the Port of Los Angeles, as the complex is known, is home to sea-centered businesses such as the headquarters of explorer Robert Ballard, who located the wrecks of the Titanic and the German battleship Bismarck. His research vessel the Nautilus docks there, as does Pacific Alliance, a vessel for farming mussels far out at sea.
On barges docked on AltaSea’s wharf, scientists from USC, UCLA and Caltech are developing methods of reducing ocean carbon dioxide and technology to scrub ships’ exhaust stacks. Other tenants in the former warehouses include startup firms that are building a new generation of remote undersea cameras and 3-D printers to build parts for offshore wind, wave and solar farms.
Jenny Cornuelle Krusoe, executive vice president and COO of AltaSea at the Port of Los Angeles.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
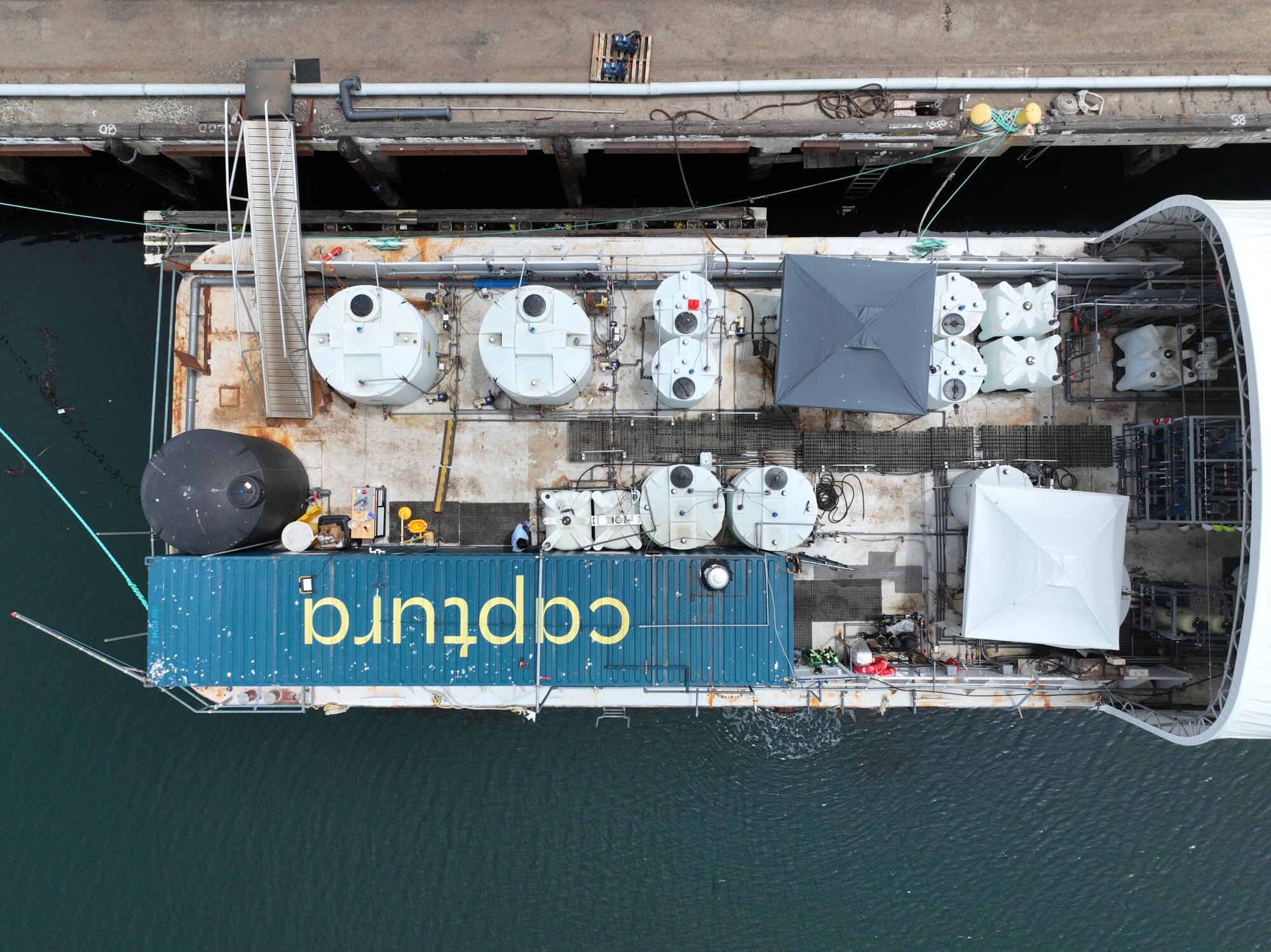

An aerial view of the Captura, a barge at AltaSea where crews monitor equipment used for pulling carbon dioxide from seawater.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
“AltaSea is education, research and business all working together,” said Jenny Krusoe, executive vice president and chief operating officer. The size and waterfront location, she added, make AltaSea “a unicorn piece of property that is basically made to be the mother ship for the blue economy.”
Mayor Karen Bass and others who played a part in AltaSea, including City Councilman Tim McOsker and Port of Los Angeles Executive Director Gene Seroka, are expected to officially open the facilities at a ceremony Wednesday.
AltaSea is bringing new purpose to a previously moribund wharf that once played a rich part in the evolution of Southern California.
In the early 20th century, Los Angeles merchants and city leaders set out to capture a share of the increased global shipping trade expected to pass through the Panama Canal, a link between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans that opened in 1914. They created a municipal wharf on the waterfront of what has become the sprawling Port of Los Angeles, with a long stretch of warehouses where ships were loaded and unloaded into trains, carts and trucks by burly longshoremen.
The growth of containerized shipping after World War II gradually rendered City Dock No. 1 obsolete for moving goods, and the wharf was little used for decades. By 2011, advocates, including port officials, saw it for what it was: a choice 35-acre site for a research center and tech companies focused on sustainable uses of the world’s oceans.
A key part of the mission of the nonprofit enterprise is to create jobs with pioneering companies. Among them is the nonprofit AltaSeads Conservancy, the largest aquaculture seed bank in the United States. Like their terrestrial counterparts, aquaculture seed banks are meant to preserve genetic diversity in plant life for the future. AltaSeads is also advancing the use of kelp as an easily grown resource.
“It’s a super versatile crop,” said scientist Emily Aguirre of AltaSeads, that can provide food for humans and livestock while removing carbon from the atmosphere. “It can be also be used to fertilize terrestrial agriculture, and it’s fantastic because if you grow it out in the ocean, you’re not taking up any land.”
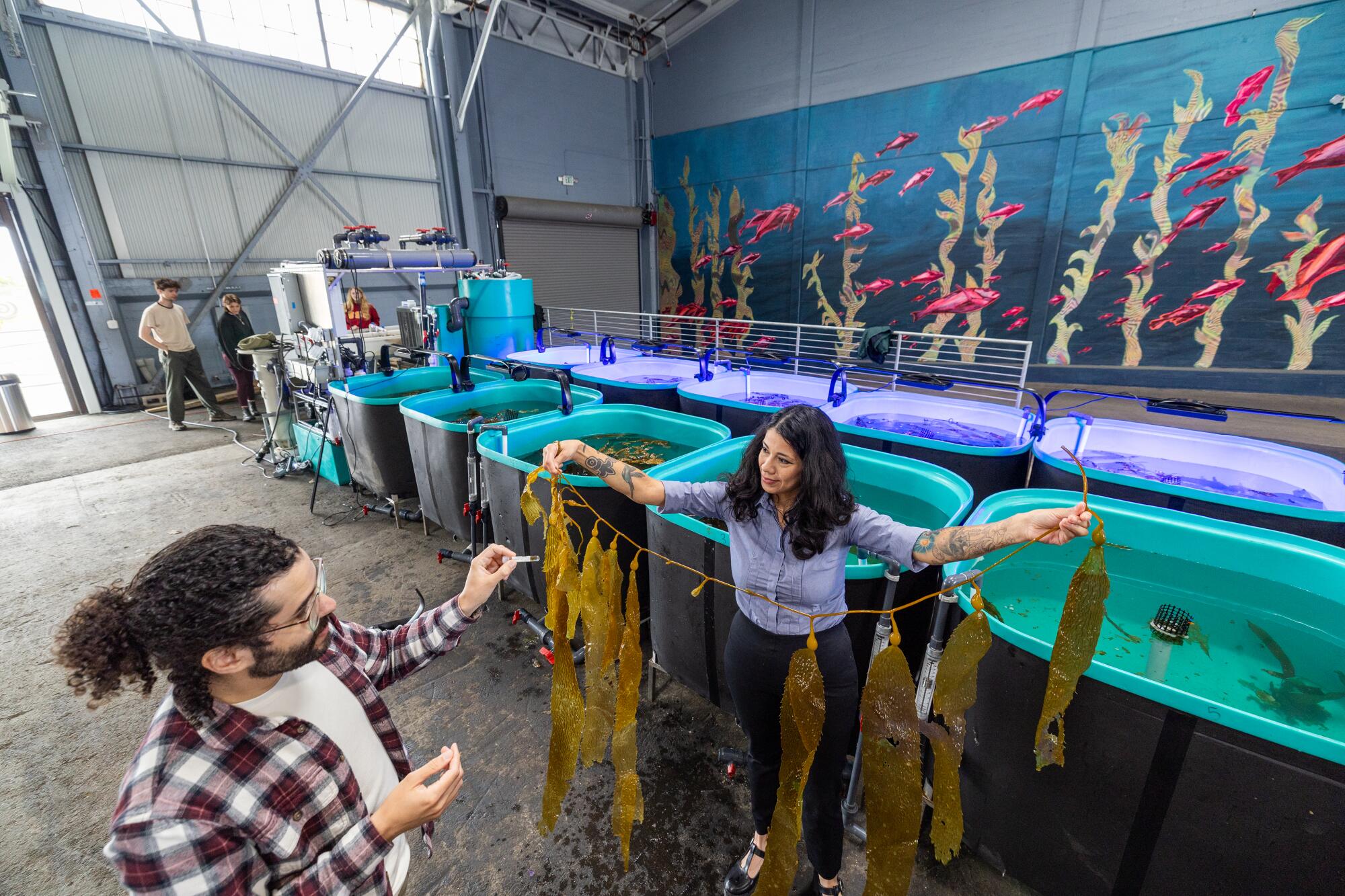

Michael Marty Rivera and Emily Aguirre of AltaSeads Conservancy monitor varieties of kelp in storage tanks.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
Kelp is also a source of algae that cuts methane emissions from cows, Aguirre said, and has many other food applications, including reducing freezer burn in ice cream.
Eco Wave Power, an Israel-based company, is set to install the first U.S. onshore wave energy pilot station in the coming months on the port’s Main Channel, next to AltaSea. The system of floaters attaches directly to preexisting structures — like breakwaters, wharfs and jetties — and produces energy from the constant motion of the waves. Another AltaSea business, CorPower Ocean, uses buoys and hydraulic pressure for energy production.
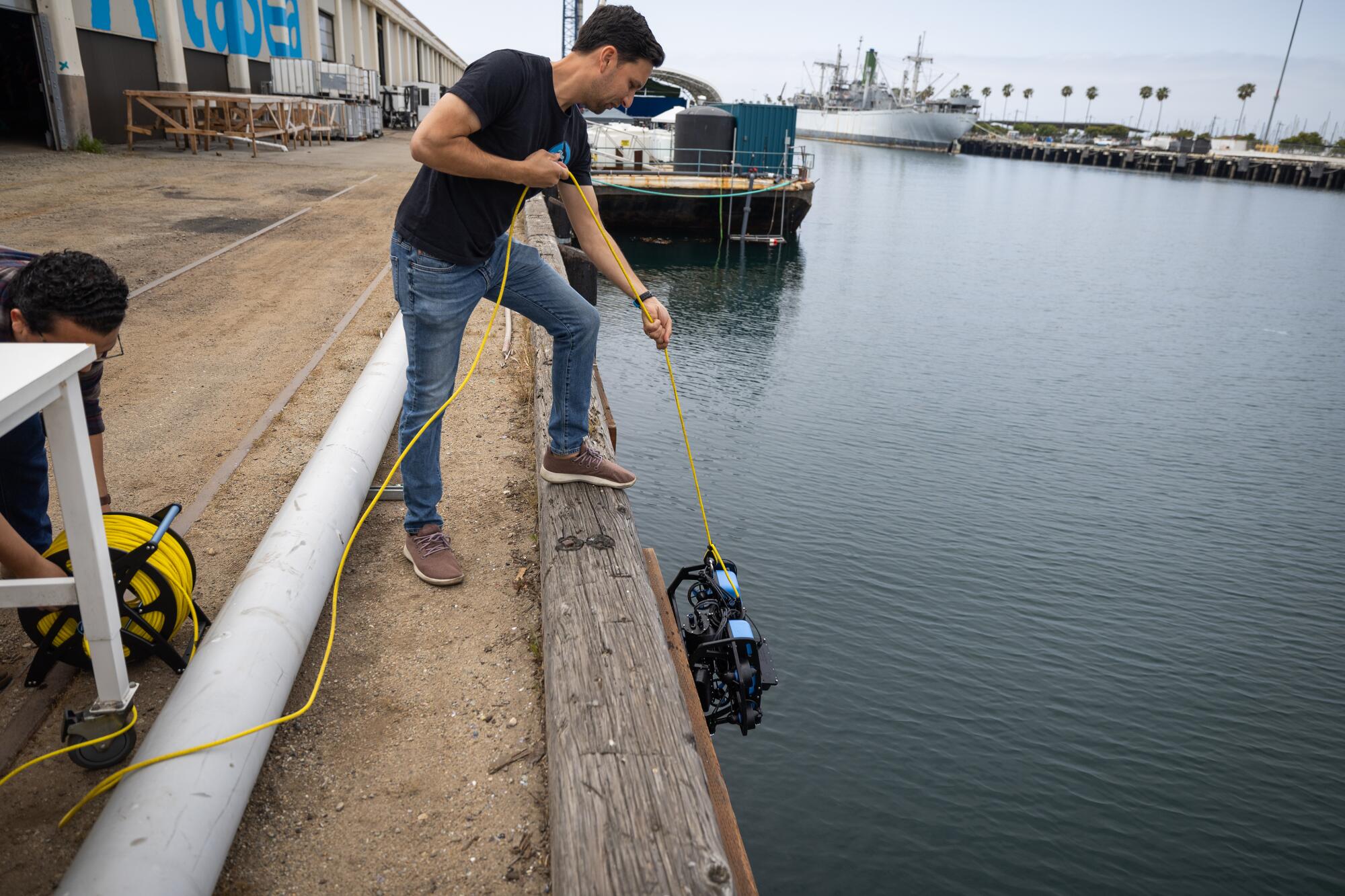

Rustom Jehangir, founder and CEO at Blue Robotics, demonstrates his BlueROV2, a high-performance remotely operated vehicle that can be used for inspections, research and adventuring.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
The figurative whale for AltaSea so far is Ballard, who set up shop at the aged docks several years ago and has captured public interest as a deep-sea explorer and scientific researcher. It’s his headquarters and home to his research and development.
AltaSea has an array of solar panels on the roof bigger than three football fields that generates 2.2 megawatts, enough to power 700 homes annually and more energy than the entire campus will need when it reaches full capacity.
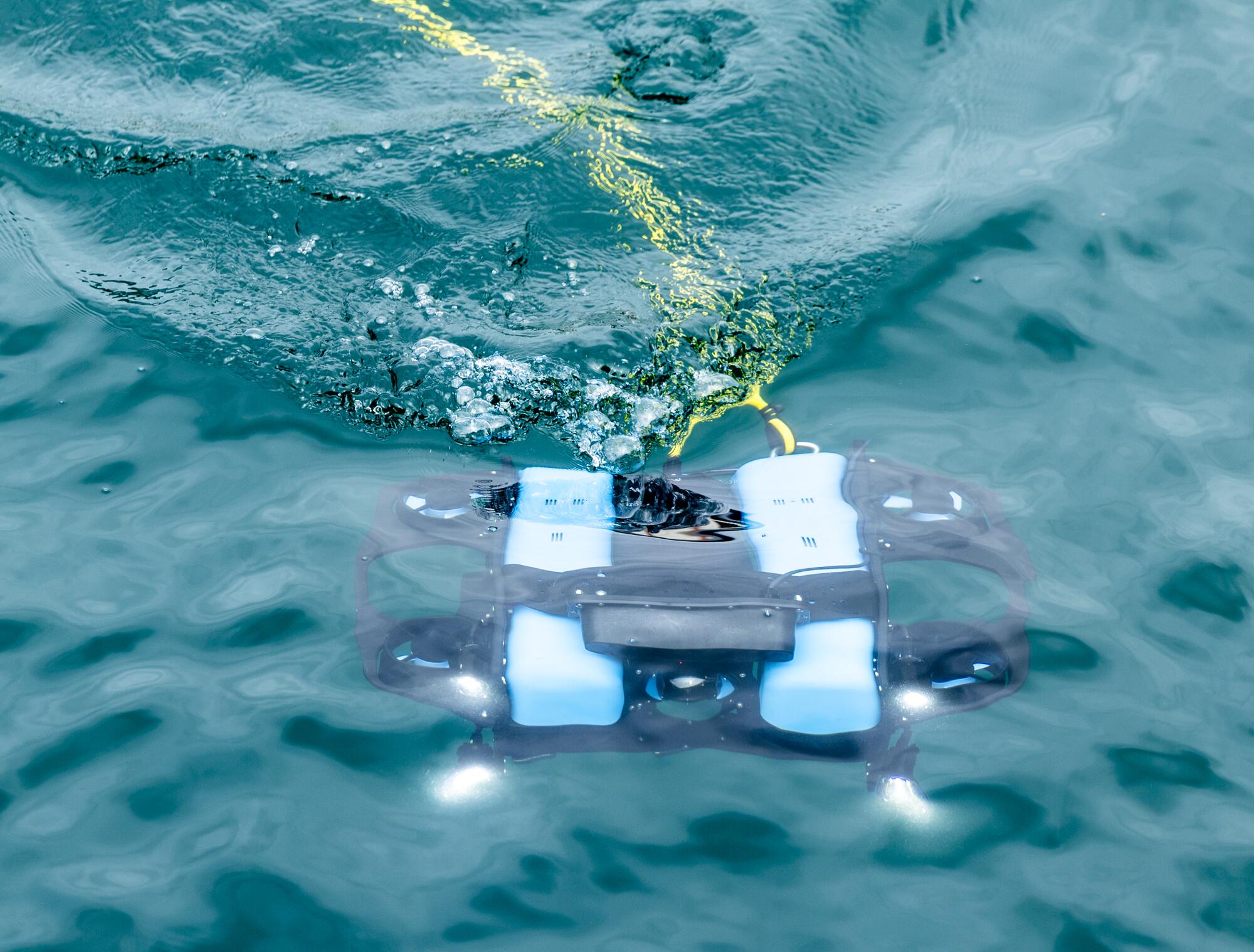
The BlueROV2 vehicle.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
To fund the wharf’s redevelopment, AltaSea received $29 million from the state, Port of Los Angeles and private donors. The funds paid for construction, installation of the solar panels and the future creation of a park.
AltaSea is one of multiple projects that are part of a two-decade process to clean up the air and water at the port and turn unused docks, wharves and warehouses into places where more people will want to work or visit, port officials said.
“Bringing people to our waterfront has been a hallmark of the Port of Los Angeles for decades,” Seroka said in 2020, and recent investments “will really bring us to the next level.”
Before the pandemic, about 3 million people came to L.A.’s waterfront annually for recreation, a tally port leaders hope to see double in the years ahead. To smooth the path of new development catering to visitors, the Port of Los Angeles is investing about $1 billion in infrastructure improvements over 10 years, Seroka said. Private developers building AltaSea and other projects will invest an estimated $500 million.
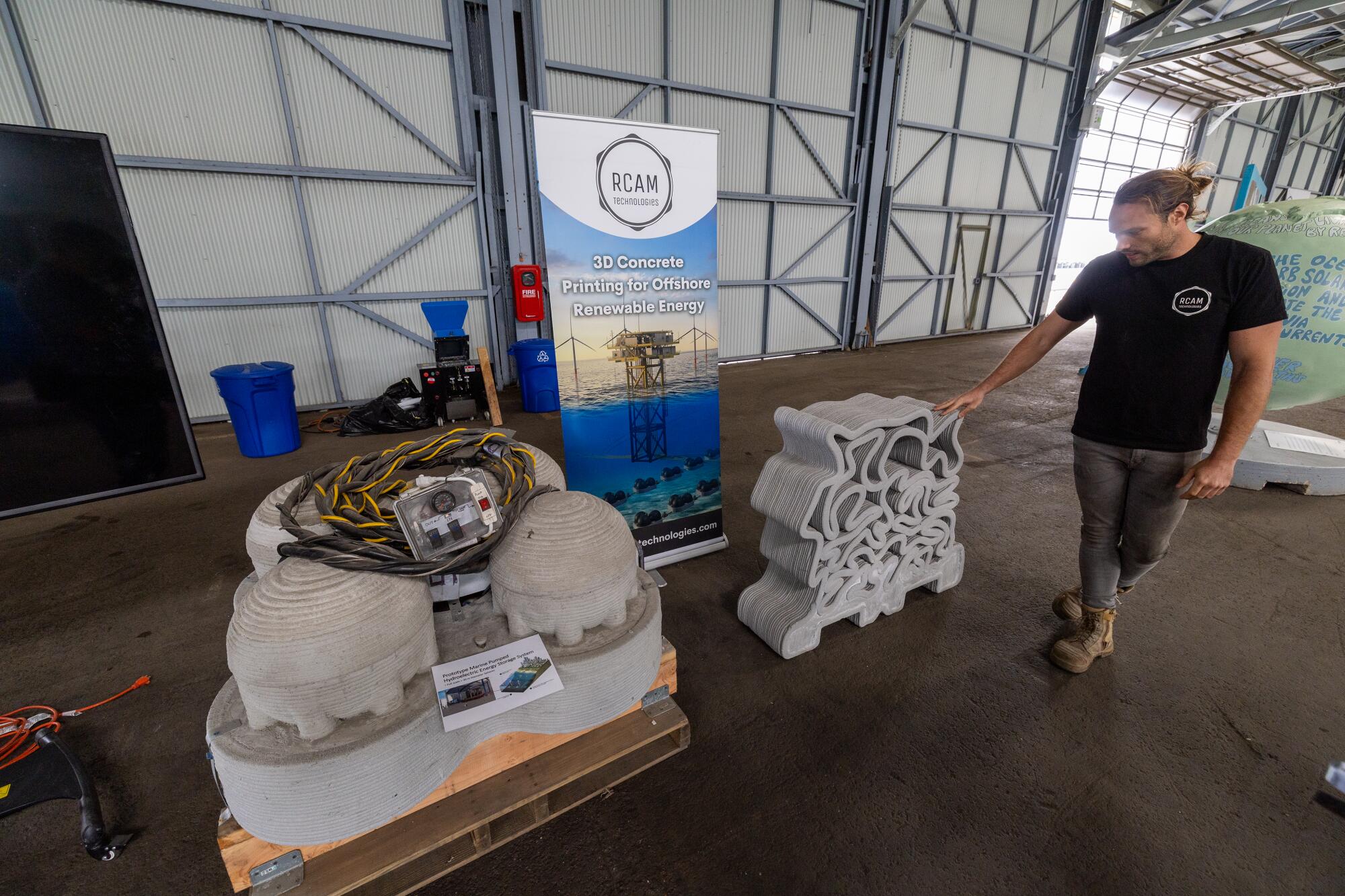

Taylor Marchment, the manufacturing R&D lead at RCAM Technologies, shows off 3-D concrete printing for offshore renewable energy.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
One of those projects, West Harbor, is a long-planned redevelopment of a 42-acre site that used to be home to Ports O’ Call, a kitschy imitation of a New England fishing village, built in the 1960s, that fell out of favor years ago and was razed in 2018.
Restaurants anchoring the dining, shopping and entertainment center will include Yamashiro, the second branch of a Japanese-themed Hollywood destination for locals and tourists. Another large restaurant will be Mexican-themed, with an over-water bar. There will also be a food hall and Bark Social, a membership off-leash dog park, bar and cafe. The complex is slated to open next year.
The waterfront developments represent improvements that San Pedro residents have been waiting decades to see, said Dustin Trani, whose family has been in the local restaurant business for nearly a century. Last year the chef opened Trani’s Dockside Station, a seafood restaurant situated between AltaSea and West Harbor, in part to capitalize on the expected influx of visitors.
“We’re on the cusp of a very big economic boom in this area that has not yet been seen,” Trani said.