World
Copper’s Price Breakout and Big Role in a Net Zero World

Copper is a metal in high demand amidst the energy transition towards net zero emissions and low carbon. This demand stems from its crucial role in powering many technologies pivotal to this transition, including renewable energy generation, electric vehicles, and efficient grid infrastructure.
Copper Prices are Breaking Out
In 2024, copper equities experienced a significant upturn, largely driven by a series of market dynamics including reductions in Chinese smelter activity, global supply concerns, and robust demand forecasts.
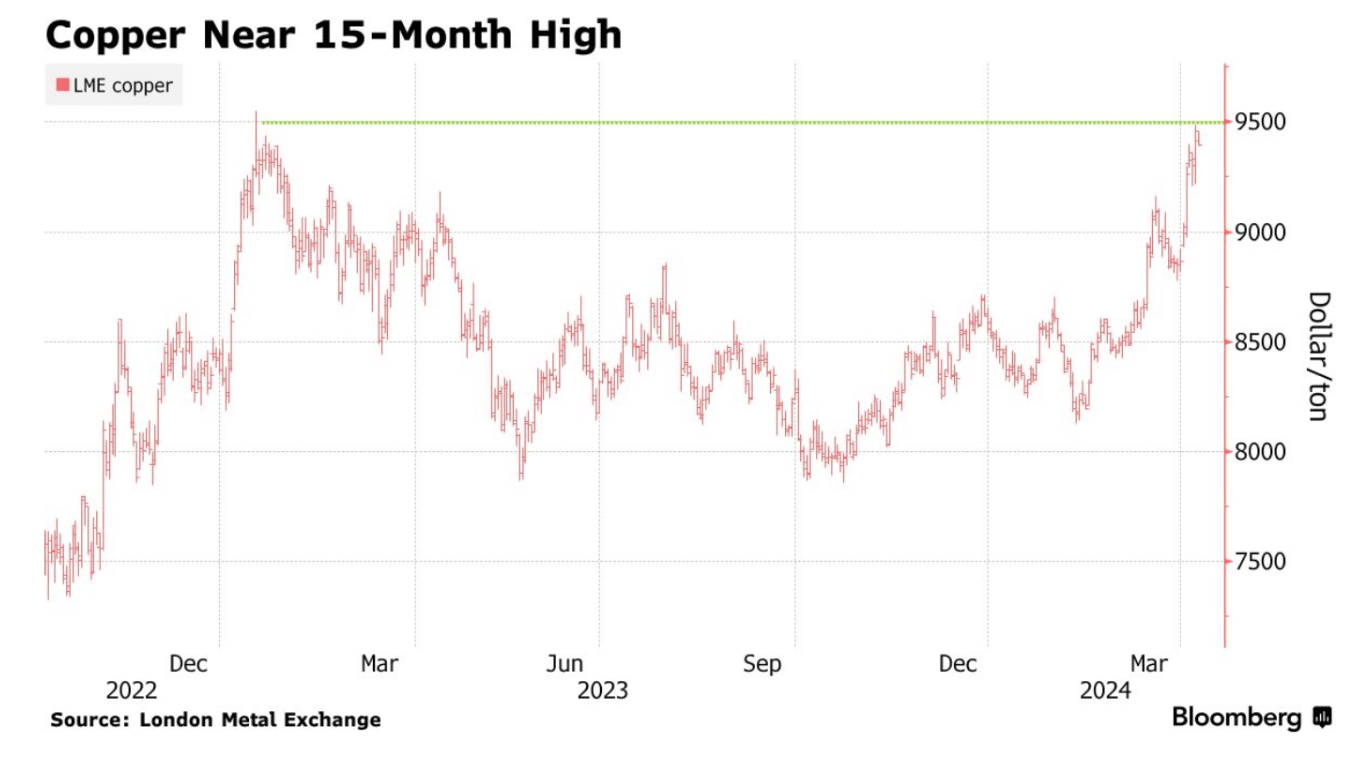
Notably, companies like Antofagasta have seen their share values surge, with the top five copper firms witnessing impressive growth. They outperform the broader materials sector.
Supply Challenges and Market Optimism
The closure of the Cobre Panama mine, a substantial global copper source, shifted market expectations from surplus to deficit, contributing to the upward price trajectory. This shift was amplified in March when Chinese smelters decided to reduce output amid a concentrate shortage, leading to a notable price increase as seen below.
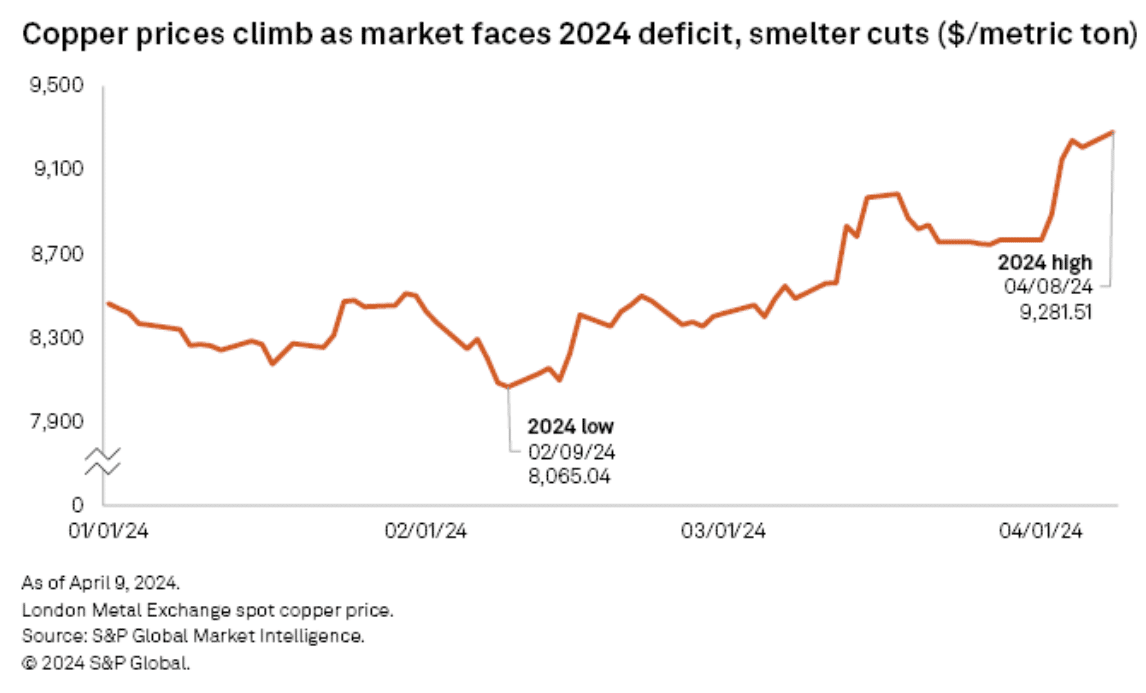

Market analysts suggest this trend reflects a mix of speculative buying and genuine supply constraints, pointing to a potentially sustained bullish market for copper.
Meanwhile, the majority of copper-focused equities are currently at or near their 52-week highs. Many are trading above consensus net asset value and analysts’ long-term copper price assumptions.
Implications for Investors and Future Demand
While the rally in copper prices is encouraging for investors, analysts caution that the market needs to validate this trend beyond short-term momentum. The sector’s performance could influence earnings, especially if copper maintains its price above $4 per pound.
Beyond immediate market mechanics, copper’s role in powering AI technology and supporting green energy transitions underscores its long-term value. This signals a sustained demand and investment interest in the metal’s future.
The Critical Role of Copper in Net Zero
Here are the detailed reasons for copper’s significance:
High Electrical Conductivity
Copper has the highest electrical conductivity rating of all non-precious metals. This property is crucial for the efficient transmission of electricity in various applications, including renewable energy technologies like solar photovoltaics (PV) and wind turbines, as well as electric vehicles (EVs) and the infrastructure that supports them, such as charging stations and the electrical grid.

Thermal Conductivity and Efficiency
Copper’s thermal efficiency is about 60% greater than aluminum, which means it can remove heat far more rapidly. This makes it ideal for use in components that generate significant amounts of heat, such as electric motors and inverters. Efficient heat dissipation is essential for maintaining the performance and longevity of these components.
Ductility and Malleability
Copper is easily shaped into wires, pipes, or sheets, which is beneficial for manufacturing a wide range of components used in renewable energy systems and EVs. Its ductility allows for the creation of fine, intricate wiring needed in advanced electrical systems.
Recyclability
Copper is 100% recyclable and can be used repeatedly without any loss of performance. This sustainability aspect is critical for the energy transition, as it supports the circular economy and reduces the need for new mining activities.
Essential Role in Renewable Energy Technologies
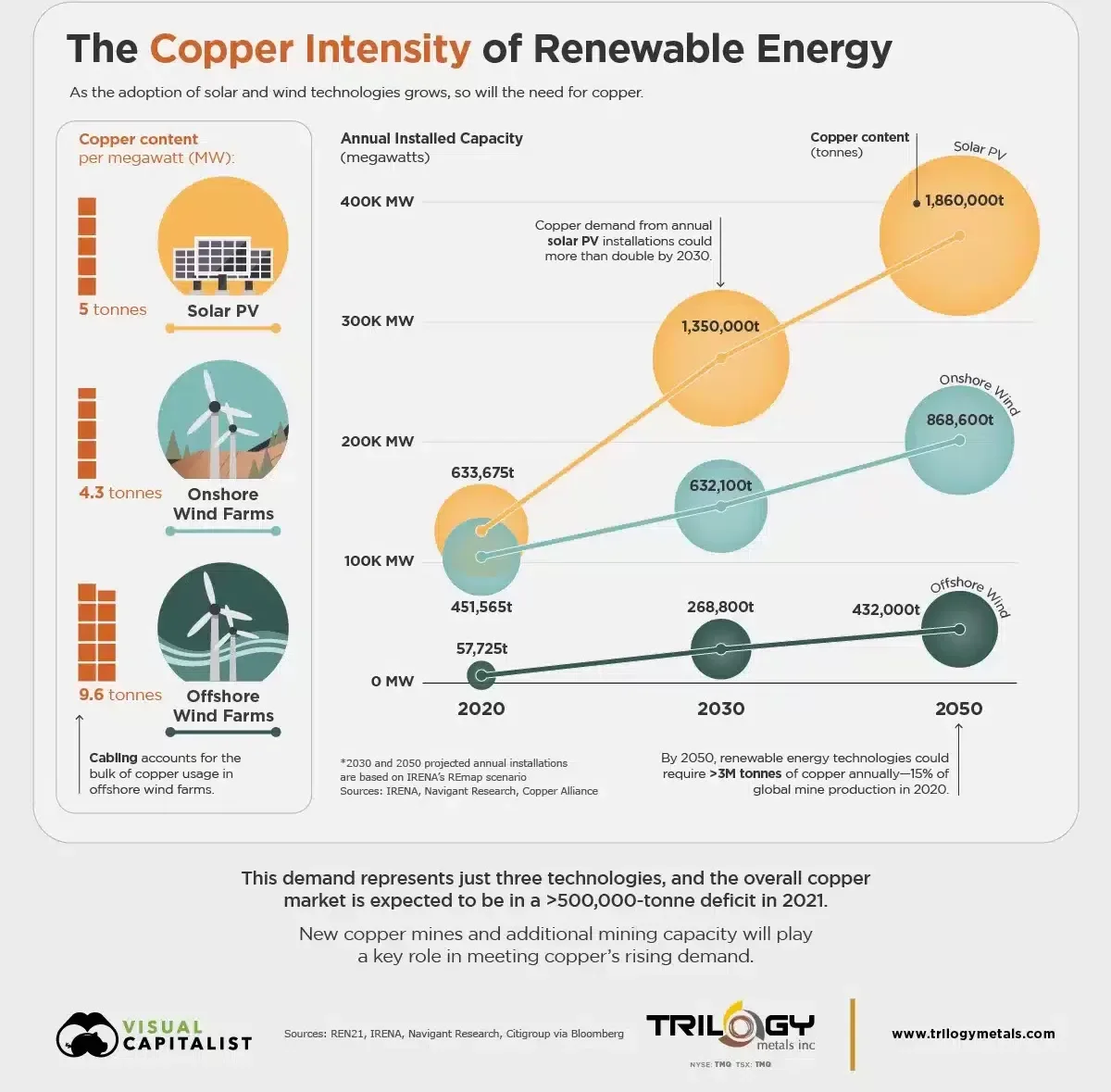
Renewable energy systems, such as solar PV and wind turbines, require significantly more copper compared to traditional energy systems. For instance, solar PV installations can use between 2,450–6,985kg of copper per megawatt of power generation, and a typical 660-kW wind turbine contains around 350kg of copper. The copper is used in the cabling, wiring, and heat exchangers that are integral to the operation of these systems.

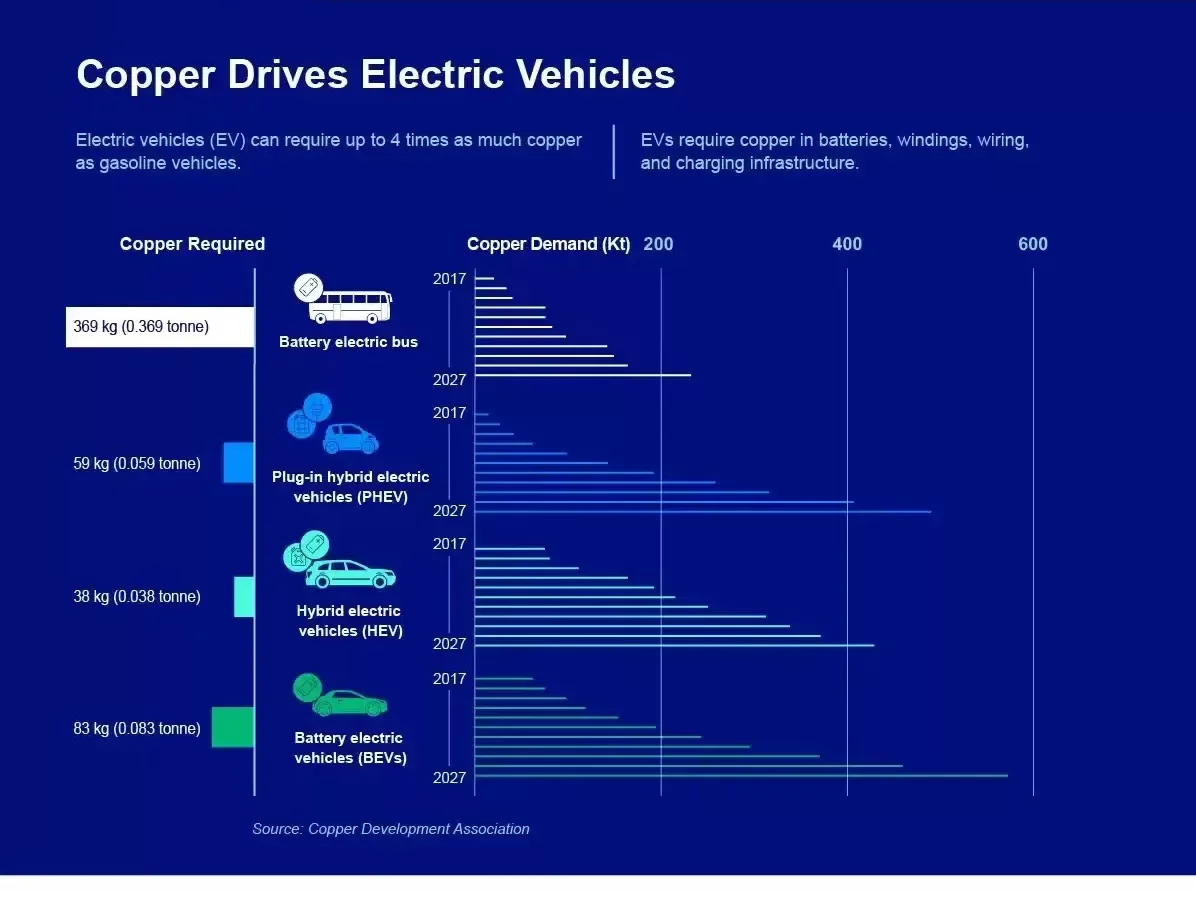
Demand in Electric Vehicles
EVs use up to four times as much copper when compared to an internal combustion engine (ICE) passenger car. Copper is used in every major EV component, from the motor to the inverter and the electrical wiring. A fully electric vehicle can use up to a mile of copper wiring, according to Wood Mackenzie.
Infrastructure Development
As the transition to renewable energy and electrification accelerates, the demand for copper in infrastructure development, such as power grids and charging stations, is expected to rise. Copper is used extensively in the electrical grid to connect renewable energy sources to consumers and in charging stations to facilitate the rapid charging of EVs.
Copper Supply and Demand Challenges for Net Zero
The demand for copper is projected to grow significantly, with estimates suggesting that it could nearly double by 2035. However, the supply of copper is not keeping pace with this demand, leading to concerns about potential shortages that could hinder the energy transition.
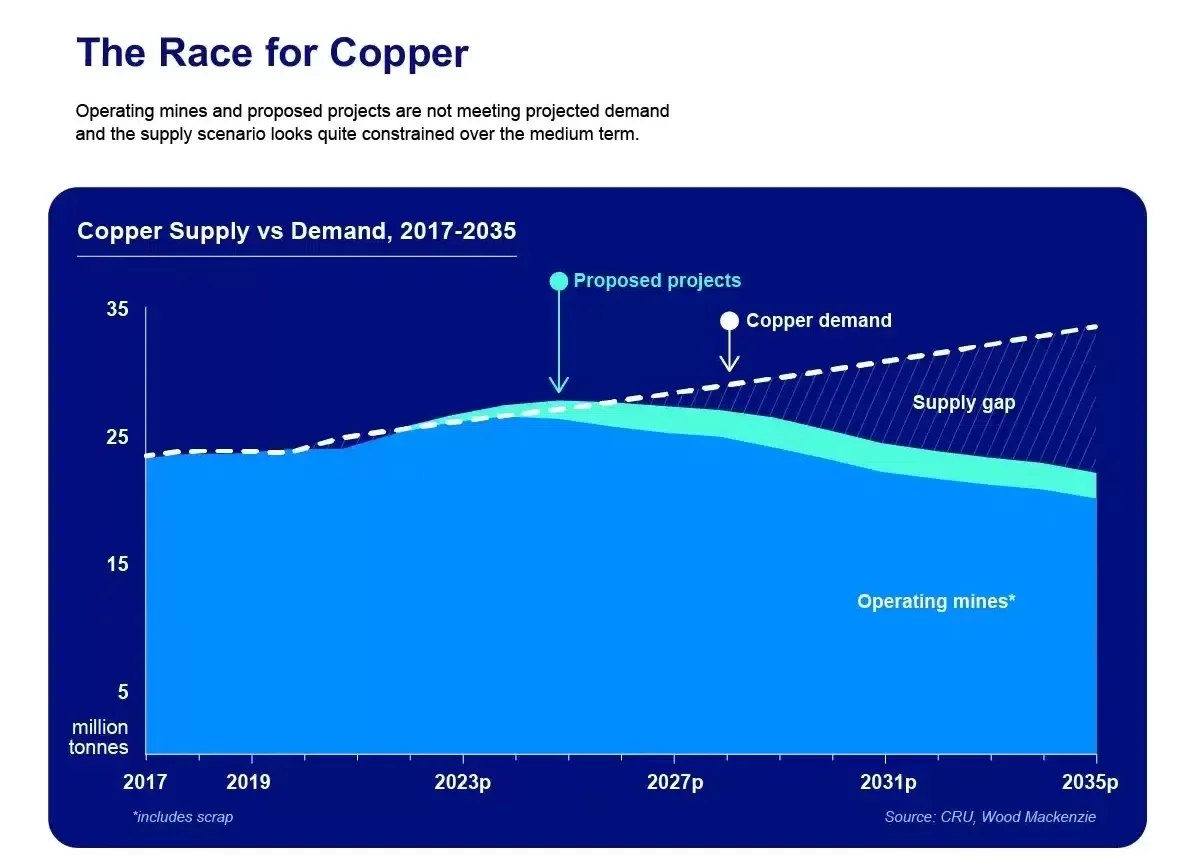

New mining initiatives and increased recycling efforts are needed to meet the growing demand for copper in the energy transition.
Copper’s unique physical properties, its role in renewable energy technologies, and its importance in the infrastructure necessary for a low-carbon future are the main reasons for its high demand in the energy transition to net zero emissions.
The challenges associated with meeting this demand underscore the need for strategic investments in copper production and recycling to support the global shift toward sustainable energy sources.








