Tech
SpaceX will attempt to catch Starship after its fifth launch
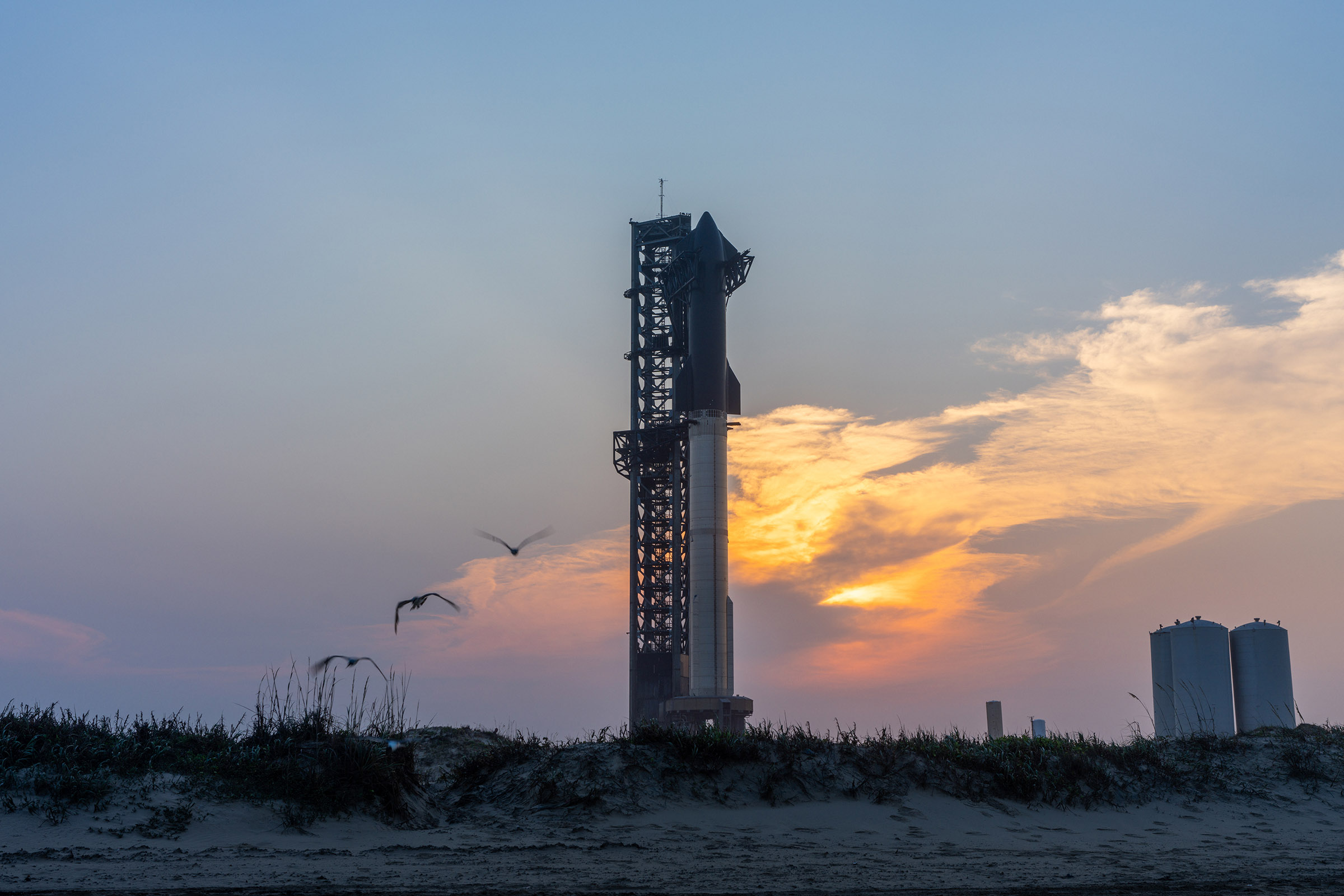

Elon Musk, the CEO of SpaceX, has shared ambitious plans for Starships’s fifth launch. The mega-rocket is slated to complete its next test launch sometime in July, following a successful fourth launch earlier this month. This time around, though, Musk says the company plans to try to “catch” the rocket on its way back down using massive robotic arms, allowing it to reuse the Super Heavy rocket.
As I noted above, it’s a very ambitious plan, but one that SpaceX needs to figure out if it wants to truly take full advantage of Starship’s capabilities. The company has already proven time and again that it can make reusable rockets happen, thanks to the success of its Falcon 9 series. However, the Super Heavy rocket doesn’t have landing legs, which means it needs another method of “landing” if it wants to reuse it.
The solution to this problem is a so-called “Mechazilla” tower, The Independent reports. Construction on the tower began in 2021, and it will measure roughly 480 feet when it is all said and done. The star of the tower is a set of robotic arms which will try to catch the rocket during Starship’s fifth launch attempt.
SpaceX says that after liftoff, the two stages will separate in flight. At that point, the Super Heavy rocket will return to the launch site, where it will reiginate its engines to slow the vehicle down, and then the arms on the tower will attempt to catch it before it re-stacks onto the orbital launch mount.
If successful, the maneuver will allow SpaceX to set up the Super Heavy rocket for another launch much quicker. The last Starship launch saw the Super Heavy rocket perform a splashdown landing. This is a major step towards achieving reusability. But Starship’s fifth launch will hold the real test for the Super Heavy rocket’s reusability.
Starship is also facing some environmental concerns, so nailing this landing will be a huge success for the team as it continues to fight uphill to prove that the mega-rocket truly is the answer to humanity’s future space exploration plans.