Even our tallest buildings can’t rival the staggering size of the world’s most iconic waterfalls, which include Niagara Falls on the U.S. border to Canada, Victoria Falls in Zimbabwe and Zambia and Angel Falls in Venezuela.
But which of these is the world’s largest waterfall?
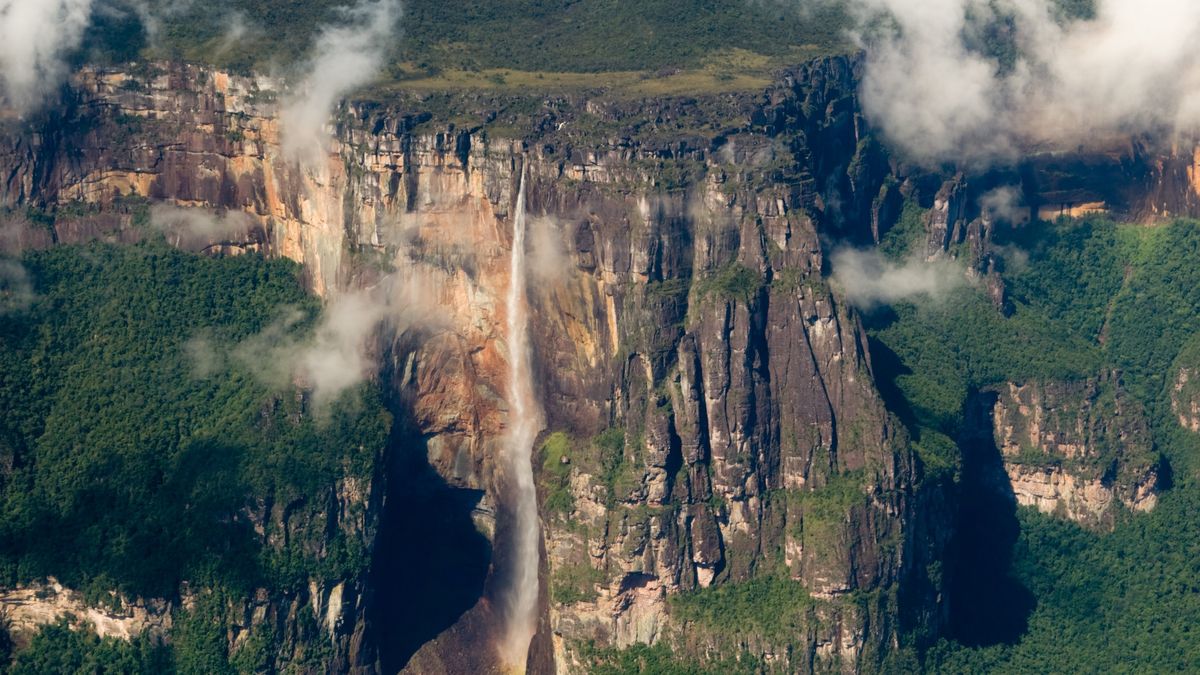
Angel Falls is the tallest waterfall on land, measuring 3,212 feet (979 meters) high and 500 feet (150 m) wide at the base, which is similar in size to three Eiffel Towers stacked on top of each other.
But technically, Angel Falls is not the biggest waterfall on Earth. That honor goes to the Denmark Strait cataract, a plunging water mass in the Denmark Strait — an ocean channel between Greenland and Iceland — meaning the world’s biggest, tallest falls are underwater.
This is possible because of the temperature and salinity gradients that power most ocean currents, according to Anna Sanchez Vidal, a professor of marine science at the University of Barcelona in Spain. The Denmark Strait straddles the Arctic Circle and acts as a funnel for polar waters flowing from the Nordic seas into the Atlantic Ocean. But like elsewhere in the ocean, the waters in this region aren’t homogeneous.
Related: What’s the largest desert in the world?
North of the Denmark Strait, surface waters that come into contact with the frigid Arctic air cool and become saltier as some of the water freezes, leading the salt to be concentrated in the nonfrozen portion. Cold, salty water is denser than warmer water and therefore sinks to the seabed, while the balmier layer rises to the surface. This exchange fuels a deep, icy current flowing southward through the strait and into the Irminger Sea in the North Atlantic Ocean.
Of course, waterfalls always feature a cliff or precipice, and the Denmark Strait is no exception. An 11,500 foot (3,500 m) drop-off in the seafloor near the southern tip of Greenland was carved out by glaciers between 17,500 and 11,500 years ago, during the last ice age. Bottom waters coursing southward through the strait hit the edge of this drop and spill down its slope, forming a cascade that dives beneath the warmer surface waters of the Irminger Sea.
The waters north of the waterfall, which scientists call the Denmark Strait cataract or overflow, are around 1,300 feet (400 m) deep, Sanchez Vidal, who led a research expedition to the strait in July and August 2023, told Live Science. Only the bottom 660 feet (200 m) cascade down the slope, she said, while the rest sits at the surface and mixes with warmer waters flowing northward through the strait. “Half of the water column is overflowing, but half is not,” she said.
Although the seabed drops by 11,500 feet, the overflow itself is smaller — around 6,600 feet (2,000 m) tall, or double the height of Angel Falls — because it lands in a deep pool of cold, dense water. The overflow is impressive, but it doesn’t look anything like a waterfall on land, said Mike Clare, leader of marine geosystems at the U.K.’s National Oceanography Centre in Southampton.
For one, the overflow is as wide as the Denmark Strait, which means it stretches across 300 miles (480 kilometers) of seabed. “It’s probably dropping about 2,000 meters vertically down into the depths of the Atlantic Ocean but over quite a big distance of something like 500 to 600 kilometers [310 to 370 miles],” Clare told Live Science. “If we visualize it, it looks like a relatively low-gradient slope.”
Related: How much does a cloud weigh?
As a result, the water streaming down the overflow reaches speeds of only around 1.6 feet per second (0.5 meter per second) — much slower than walking speed and a far cry from the speeds recorded at Niagara Falls, where water plunges down at 68 mph (109 km/h), or 100 feet per second (30.5 m/s).
“If you were down there, you probably wouldn’t notice a whole heap going on,” Clare said.
The same goes for above the waves, where there are no signs that reveal the underwater cascade, Sanchez Vidal said. “At the surface, you have typical sunny Arctic conditions,” she said, and “you cannot see anything from space” except through mapping indicators, such as temperature and salinity.
But looks are deceiving. Cold waters gliding through the Denmark Strait are part of a vital system of ocean currents known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which carries warm waters north and cold waters south in a long loop within the Atlantic Ocean. After cold water exits the Denmark Strait, it continues its journey south to the Antarctic, then warms up and rises to the surface in a process called upwelling before returning north to complete the cycle in the Arctic.
The AMOC transports much more than water molecules, Clare said. Its cold, bottom currents inject oxygen, nutrients and organic matter into the ocean depths, providing food for a rich array of deep-sea life. The Denmark Strait overflow sits at the base of this life-supporting system — so, while “visually it doesn’t look that impressive, realistically it is a hugely impressive feature in terms of the role it plays in the global ocean,” he said.
Unfortunately, the overflow is under threat from climate change, Sanchez Vidal said. Melting ice caps and warming oceans are pumping fresh water into the system and slowing the AMOC, which scientists say is inching closer to a tipping point. Should the AMOC grind to a halt, the Denmark Strait overflow “will decrease in density and it will stop,” she said.
The Denmark Strait overflow isn’t the only known underwater cascade. In fact, there are features on the seafloor called knickpoints that look a lot more like waterfalls on land, Clare said. Knickpoints often occur on continental margins, where water flows transporting sediments carve out submarine canyons.
“They’re actually much faster than the flows we see in the Denmark Strait,” he said, “and at the bottom, we do get features a bit like plunge pools that you get in waterfalls.”










